La enfermedad placentaria produce consecuencias sobre el cerebro fetal y el recién nacido, y es necesario conocer algunas de las patologías placentarias que pueden ser responsables de problemas neurológicos futuros.
Placentopatías agudas.
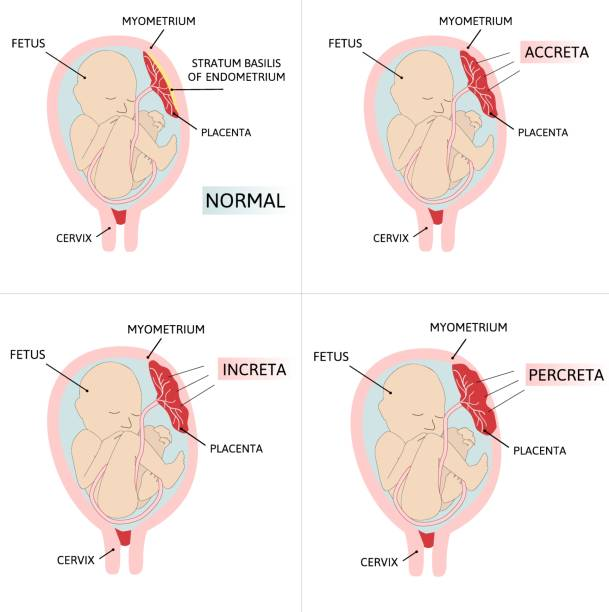
Localización de la implantación placentaria

Desprendimiento de placenta
Placentopatías crónicas.
Placenta pequeña/grande para edad gestacional
332710
{332710:24LP2P7K}
1
vancouver
50
default
3443
https://neuropediatoolkit.org/wp-content/plugins/zotpress/
%7B%22status%22%3A%22success%22%2C%22updateneeded%22%3Afalse%2C%22instance%22%3Afalse%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22request_last%22%3A0%2C%22request_next%22%3A0%2C%22used_cache%22%3Atrue%7D%2C%22data%22%3A%5B%7B%22key%22%3A%2224LP2P7K%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A332710%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Roberts%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222017%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BRoberts%20DJ%2C%20Redline%20RW%2C%20Boyd%20TK%2C%20editors.%20Placental%20Weights%3A%20Means%2C%20Standard%20Deviations%2C%20and%20Percentiles%20by%20Gestational%20Age.%20In%3A%20Placental%20and%20Gestational%20Pathology%20%5BInternet%5D.%20Cambridge%3A%20Cambridge%20University%20Press%3B%202017%20%5Bcited%202022%20Nov%201%5D.%20p.%20336%26%23x2013%3B336.%20%28Diagnostic%20Pediatric%20Pathology%29.%20Available%20from%3A%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.cambridge.org%5C%2Fcore%5C%2Fbooks%5C%2Fplacental-and-gestational-pathology%5C%2Fplacental-weights-means-standard-deviations-and-percentiles-by-gestational-age%5C%2F6D7F30DA21FF2CE00EB4D14FF1E7B1DE%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.cambridge.org%5C%2Fcore%5C%2Fbooks%5C%2Fplacental-and-gestational-pathology%5C%2Fplacental-weights-means-standard-deviations-and-percentiles-by-gestational-age%5C%2F6D7F30DA21FF2CE00EB4D14FF1E7B1DE%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22bookSection%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Placental%20Weights%3A%20Means%2C%20Standard%20Deviations%2C%20and%20Percentiles%20by%20Gestational%20Age%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Drucilla%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Roberts%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Raymond%20W.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Redline%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Theonia%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Boyd%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22bookTitle%22%3A%22Placental%20and%20Gestational%20Pathology%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222017%22%2C%22originalDate%22%3A%22%22%2C%22originalPublisher%22%3A%22%22%2C%22originalPlace%22%3A%22%22%2C%22format%22%3A%22%22%2C%22ISBN%22%3A%22978-1-316-85933-9%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1017%5C%2F9781316848616.039%22%2C%22citationKey%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.cambridge.org%5C%2Fcore%5C%2Fbooks%5C%2Fplacental-and-gestational-pathology%5C%2Fplacental-weights-means-standard-deviations-and-percentiles-by-gestational-age%5C%2F6D7F30DA21FF2CE00EB4D14FF1E7B1DE%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%22%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22HKPR6S6M%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222025-09-04T16%3A45%3A54Z%22%7D%7D%5D%7D
1.
Roberts DJ, Redline RW, Boyd TK, editors. Placental Weights: Means, Standard Deviations, and Percentiles by Gestational Age. In: Placental and Gestational Pathology [Internet]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2017 [cited 2022 Nov 1]. p. 336–336. (Diagnostic Pediatric Pathology). Available from: https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/placental-and-gestational-pathology/placental-weights-means-standard-deviations-and-percentiles-by-gestational-age/6D7F30DA21FF2CE00EB4D14FF1E7B1DE
Tipos de implantación placentaria

RCIU y feto pequeño para edad gestacional.

332710
{332710:8NJUXPR3},{332710:HTAG3HHS},{332710:DFHCTLC2}
1
vancouver
50
default
3443
https://neuropediatoolkit.org/wp-content/plugins/zotpress/
%7B%22status%22%3A%22success%22%2C%22updateneeded%22%3Afalse%2C%22instance%22%3Afalse%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22request_last%22%3A0%2C%22request_next%22%3A0%2C%22used_cache%22%3Atrue%7D%2C%22data%22%3A%5B%7B%22key%22%3A%228NJUXPR3%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A332710%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Gardella%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222022%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BGardella%20B%2C%20Dominoni%20M%2C%20Scatigno%20AL%2C%20Cesari%20S%2C%20Fiandrino%20G%2C%20Orcesi%20S%2C%20et%20al.%20What%20is%20known%20about%20neuroplacentology%20in%20fetal%20growth%20restriction%20and%20in%20preterm%20infants%3A%20A%20narrative%20review%20of%20literature.%20Frontiers%20in%20Endocrinology%20%5BInternet%5D.%202022%20%5Bcited%202022%20Nov%201%5D%3B13.%20Available%20from%3A%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.frontiersin.org%5C%2Farticles%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffendo.2022.936171%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.frontiersin.org%5C%2Farticles%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffendo.2022.936171%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22What%20is%20known%20about%20neuroplacentology%20in%20fetal%20growth%20restriction%20and%20in%20preterm%20infants%3A%20A%20narrative%20review%20of%20literature%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Barbara%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gardella%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mattia%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dominoni%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Annachiara%20Licia%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Scatigno%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Stefania%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Cesari%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Giacomo%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fiandrino%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Simona%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Orcesi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Arsenio%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Spinillo%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22The%20placenta%20plays%20a%20fundamental%20role%20during%20pregnancy%20for%20fetal%20growth%20and%20development.%20A%20suboptimal%20placental%20function%20may%20result%20in%20severe%20consequences%20during%20the%20infant%5Cu2019s%20first%20years%20of%20life.%20In%20recent%20years%2C%20a%20new%20field%20known%20as%20neuroplacentology%20has%20emerged%20and%20it%20focuses%20on%20the%20role%20of%20the%20placenta%20in%20fetal%20and%20neonatal%20brain%20development.%20Because%20of%20the%20limited%20data%2C%20our%20aim%20was%20to%20provide%20a%20narrative%20review%20of%20the%20most%20recent%20knowledge%20about%20the%20relation%20between%20placental%20lesions%20and%20fetal%20and%20newborn%20neurological%20development.%20Papers%20published%20online%20from%202000%20until%20February%202022%20were%20taken%20into%20consideration%20and%20particular%20attention%20was%20given%20to%20articles%20in%20which%20placental%20lesions%20were%20related%20to%20neonatal%20morbidity%20and%20short-term%20and%20long-term%20neurological%20outcome.%20Most%20research%20regarding%20the%20role%20of%20placental%20lesions%20in%20neurodevelopment%20has%20been%20conducted%20on%20fetal%20growth%20restriction%20and%20preterm%20infants.%20Principal%20neurological%20outcomes%20investigated%20were%20periventricular%20leukomalacia%2C%20intraventricular%20hemorrhages%2C%20neonatal%20encephalopathy%20and%20autism%20spectrum%20disorder.%20No%20consequences%20in%20motor%20development%20were%20found.%20All%20the%20considered%20studies%20agree%20about%20the%20crucial%20role%20played%20by%20placenta%20in%20fetal%20and%20neonatal%20neurological%20development%20and%20outcome.%20However%2C%20the%20causal%20mechanisms%20remain%20largely%20unknown.%20Knowledge%20on%20the%20pathophysiological%20mechanisms%20and%20on%20placenta-related%20risks%20for%20neurological%20problems%20may%20provide%20clues%20for%20early%20interventions%20aiming%20to%20improve%20neurological%20outcomes%2C%20especially%20among%20pediatricians%20and%20child%20psychiatrists.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222022%22%2C%22section%22%3A%22%22%2C%22partNumber%22%3A%22%22%2C%22partTitle%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3389%5C%2Ffendo.2022.936171%22%2C%22citationKey%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.frontiersin.org%5C%2Farticles%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffendo.2022.936171%22%2C%22PMID%22%3A%22%22%2C%22PMCID%22%3A%22%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221664-2392%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22HKPR6S6M%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222025-04-22T17%3A21%3A36Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22DFHCTLC2%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A332710%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Mir%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222021-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BMir%20IN%2C%20Leon%20R%2C%20Chalak%20LF.%20Placental%20origins%20of%20neonatal%20diseases%3A%20toward%20a%20precision%20medicine%20approach.%20Pediatr%20Res%20%5BInternet%5D.%202021%20Jan%20%5Bcited%202022%20Nov%201%5D%3B89%282%29%3A377%26%23x2013%3B83.%20Available%20from%3A%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.nature.com%5C%2Farticles%5C%2Fs41390-020-01293-6%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.nature.com%5C%2Farticles%5C%2Fs41390-020-01293-6%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Placental%20origins%20of%20neonatal%20diseases%3A%20toward%20a%20precision%20medicine%20approach%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Imran%20N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mir%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Rachel%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Leon%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lina%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chalak%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22The%20placenta%20is%20the%20single%20most%20reliable%20source%20for%20precise%20information%20on%20intrauterine%20environment%2C%20as%20well%20as%20maternal%20and%20fetal%20health.%20It%20mediates%20the%20physiology%20of%20two%20distinct%20yet%20highly%20interconnected%20individuals.%20The%20pathology%20that%20develops%20in%20the%20placenta%2C%20and%20the%20adaptations%20the%20placenta%20undergoes%20to%20mitigate%20this%20pathology%2C%20may%20influence%20the%20later%20life%20health%20of%20the%20mother%20and%20baby.%20Pathological%20placental%20examination%20provides%20a%20unique%20opportunity%20to%20explore%20and%20understand%20the%20intrauterine%20environment%2C%20as%20well%20as%20providing%20a%20record%20of%20events%20that%20may%20be%20associated%20with%20adverse%20pregnancy%20outcomes.%20A%20number%20of%20placental%20lesions%20have%20been%20described%20in%20association%20with%20various%20neonatal%20morbidities.%20The%20purpose%20of%20this%20review%20is%20to%20summarize%20the%20evidence%20for%20the%20association%20of%20placental%20pathologic%20lesions%20with%20neurodevelopmental%20outcomes%20infants%20with%20specific%20neonatal%20morbidities%2C%20including%20%281%29%20neonatal%20encephalopathy%2C%20%282%29%20bronchopulmonary%20dysplasia%2C%20%283%29%20congenital%20heart%20diseases%2C%20and%20%284%29%20autism%20spectrum%20disorders.%20For%20each%20of%20these%20disease%20processes%2C%20we%20will%20also%20propose%20specific%20research%20priorities%20in%20future%20studies.%20We%20conclude%20with%20a%20hospital-specific%20protocol%20for%20triaging%20which%20placentas%20should%20receive%20histological%20evaluation%20as%20a%20fundamental%20first%20step%20for%20the%20field%20of%20neuroplacentology%20to%20guide%20precision-based%20therapeutic%20approaches%20in%20the%20affected%20newborns.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222021-01%22%2C%22section%22%3A%22%22%2C%22partNumber%22%3A%22%22%2C%22partTitle%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1038%5C%2Fs41390-020-01293-6%22%2C%22citationKey%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.nature.com%5C%2Farticles%5C%2Fs41390-020-01293-6%22%2C%22PMID%22%3A%22%22%2C%22PMCID%22%3A%22%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221530-0447%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22HKPR6S6M%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222025-04-22T08%3A23%3A40Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22HTAG3HHS%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A332710%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Leon%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222022-03%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BLeon%20RL%2C%20Mir%20IN%2C%20Herrera%20CL%2C%20Sharma%20K%2C%20Spong%20CY%2C%20Twickler%20DM%2C%20et%20al.%20Neuroplacentology%20in%20congenital%20heart%20disease%3A%20placental%20connections%20to%20neurodevelopmental%20outcomes.%20Pediatr%20Res%20%5BInternet%5D.%202022%20Mar%20%5Bcited%202022%20Nov%201%5D%3B91%284%29%3A787%26%23x2013%3B94.%20Available%20from%3A%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.nature.com%5C%2Farticles%5C%2Fs41390-021-01521-7%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.nature.com%5C%2Farticles%5C%2Fs41390-021-01521-7%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Neuroplacentology%20in%20congenital%20heart%20disease%3A%20placental%20connections%20to%20neurodevelopmental%20outcomes%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Rachel%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Leon%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Imran%20N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mir%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Christina%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Herrera%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kavita%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sharma%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Catherine%20Y.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Spong%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Diane%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Twickler%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lina%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chalak%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Children%20with%20congenital%20heart%20disease%20%28CHD%29%20are%20living%20longer%20due%20to%20effective%20medical%20and%20surgical%20management.%20However%2C%20the%20majority%20have%20neurodevelopmental%20delays%20or%20disorders.%20The%20role%20of%20the%20placenta%20in%20fetal%20brain%20development%20is%20unclear%20and%20is%20the%20focus%20of%20an%20emerging%20field%20known%20as%20neuroplacentology.%20In%20this%20review%2C%20we%20summarize%20neurodevelopmental%20outcomes%20in%20CHD%20and%20their%20brain%20imaging%20correlates%20both%20in%20utero%20and%20postnatally.%20We%20review%20differences%20in%20the%20structure%20and%20function%20of%20the%20placenta%20in%20pregnancies%20complicated%20by%20fetal%20CHD%20and%20introduce%20the%20concept%20of%20a%20placental%20inefficiency%20phenotype%20that%20occurs%20in%20severe%20forms%20of%20fetal%20CHD%2C%20characterized%20by%20a%20myriad%20of%20pathologies.%20We%20propose%20that%20in%20CHD%20placental%20dysfunction%20contributes%20to%20decreased%20fetal%20cerebral%20oxygen%20delivery%20resulting%20in%20poor%20brain%20growth%2C%20brain%20abnormalities%2C%20and%20impaired%20neurodevelopment.%20We%20conclude%20the%20review%20with%20key%20areas%20for%20future%20research%20in%20neuroplacentology%20in%20the%20fetal%20CHD%20population%2C%20including%20%281%29%20differences%20in%20structure%20and%20function%20of%20the%20CHD%20placenta%2C%20%282%29%20modifiable%20and%20nonmodifiable%20factors%20that%20impact%20the%20hemodynamic%20balance%20between%20placental%20and%20cerebral%20circulations%2C%20%283%29%20interventions%20to%20improve%20placental%20function%20and%20protect%20brain%20development%20in%20utero%2C%20and%20%284%29%20the%20role%20of%20genetic%20and%20epigenetic%20influences%20on%20the%20placenta%5Cu2013heart%5Cu2013brain%20connection.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222022-03%22%2C%22section%22%3A%22%22%2C%22partNumber%22%3A%22%22%2C%22partTitle%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1038%5C%2Fs41390-021-01521-7%22%2C%22citationKey%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.nature.com%5C%2Farticles%5C%2Fs41390-021-01521-7%22%2C%22PMID%22%3A%22%22%2C%22PMCID%22%3A%22%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221530-0447%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22HKPR6S6M%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222025-04-22T08%3A19%3A29Z%22%7D%7D%5D%7D
1.
Gardella B, Dominoni M, Scatigno AL, Cesari S, Fiandrino G, Orcesi S, et al. What is known about neuroplacentology in fetal growth restriction and in preterm infants: A narrative review of literature. Frontiers in Endocrinology [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2022 Nov 1];13. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2022.936171
1.
Mir IN, Leon R, Chalak LF. Placental origins of neonatal diseases: toward a precision medicine approach. Pediatr Res [Internet]. 2021 Jan [cited 2022 Nov 1];89(2):377–83. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41390-020-01293-6
1.
Leon RL, Mir IN, Herrera CL, Sharma K, Spong CY, Twickler DM, et al. Neuroplacentology in congenital heart disease: placental connections to neurodevelopmental outcomes. Pediatr Res [Internet]. 2022 Mar [cited 2022 Nov 1];91(4):787–94. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41390-021-01521-7